Lumen Connection Fail. Please Try Again.
TL;DR: In this tutorial, I'll show y'all how piece of cake it is to build and secure an API with Lumen. Check out the repo to get the code.
Lumen is an open-source PHP micro-framework created by Taylor Otwell every bit an alternative to Laravel to see the demand of lightweight installations that are faster than existing PHP micro-frameworks such as Slim and Silex. With Lumen, y'all tin build lightning-fast microservices and APIs that can back up your Laravel applications.
Lumen Features and Compages
Lumen utilizes the Illuminate components that ability the Laravel framework. Equally such, Lumen is built to painlessly upgrade directly to Laravel when needed; for example, when you discover that you demand more features out of the box than what Lumen offers.
These are some of the congenital-in features of Lumen:
-
Routing is provided out of the box in Lumen. This includes bones routing, routing parameters, named routes, and route groups such as middleware.
-
Authentication does non support session state. However, incoming requests are authenticated via stateless mechanisms such every bit tokens.
-
Caching is implemented the same as in Laravel. Cache drivers such as Database, Memcached, and Redis are supported. For example, you can install the
illuminate/redispackage via Composer to use a Redis enshroud with Lumen. -
Errors and Logging are implemented via the Monolog library, which provides support for various log handlers.
-
Queuing services are similar to the ones offered by Laravel. A unified API is provided beyond a variety of unlike queue back-ends.
-
Events provide a uncomplicated observer implementation that allows you to subscribe and mind for events in your application.
-
Bootstrapping processes are located in a single file.
"Lumen is an amazing PHP micro-framework that offers a painless upgrade path to Laravel."

Tweet This
Lumen Key Requirements
To use Lumen, you demand to take the following tools installed on your machine:
- PHP: Brand sure
PHP >= vii.twois installed on your machine. Furthermore, ensure that the following PHP extensions are installed.OpenSSL,PDOandMbstring. - Composer: Navigate to the Composer website and install information technology on your machine. Composer is needed to install Lumen'south dependencies.
Note: You'll need MySQL for this tutorial. Navigate to the MySQL website and install the community server edition. If you are using a Mac, I recommend following these instructions. For this tutorial, you tin can use MySQL directly from the terminal, but if y'all'd prefer a MySQL GUI, check out Sequel Pro for Mac or HeidiSQL for Windows.
At Auth0, nosotros have many technical writers, otherwise known every bit authors. A directive has been given to developing an app to manage Auth0 authors. The front-end app will be built with ReactJS. All the same, it needs to pull data from a source and as well push to it. Yes, we need an API!
This is what we need the API to do:
- Get all authors.
- Go i writer.
- Add together a new author.
- Edit an writer.
- Delete an writer.
Let'due south flesh out the possible endpoints for this API. Given some authors resource, we'll have the following endpoints:
- Get all authors -
Get /api/authors - Get one author -
Become /api/authors/ 23 - Create an author -
Mail /api/authors - Edit an writer -
PUT /api/authors/ 23 - Delete an author -
DELETE /api/authors/ 23
What will exist the author attributes? Let's mankind it out similar nosotros did the endpoints.
- Writer:
proper noun,email,twitter,github,location, andlatest_article_published.
Install Lumen
Run the following control in your last to create a new project with Lumen:
composer create-projection --adopt-dist laravel/lumen authors cd into the newly created project.
cd authors Now, run php - South localhost: 8000 -t public to serve the project. Head over to your browser. You should see the alphabetize page similar and then:
Activate Eloquent and Facades
Every bit I mentioned earlier, the unabridged bootstrap process is located in a single file.
Open the bootstrap/app.php and uncomment this line, // app->withEloquent . Once uncommented, Lumen hooks the Eloquent ORM with your database using the connections configured in the .env file.
Make sure yous prepare the right details for your database in the .env file.
Side by side uncomment this line //$app->withFacades(); , which allows u.s.a. to make apply of Facades in our projection.
Setup Database, Models and Migrations
At the time of this writing, Lumen supports four database systems: MySQL, Postgres, SQLite, and SQL Server. Nosotros are making use of MySQL in this tutorial. Get-go, we'll create a migration for the authors tabular array.
Migrations are similar version command for your database, allowing your team to easily change and share the application's database schema.
Run the control below in the terminal to create the authors table migration:
php artisan make:migration create_authors_table The new migration will be placed in your database/migrations directory. Each migration file name contains a timestamp, which allows Lumen to determine the club of the migrations. Adjacent, we'll modify the recently created migration to include the attributes we demand for the authors tabular array.
Open up the migration file and modify it like and then:
<?php apply Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema ; use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint ; use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration ; grade CreateAuthorsTable extends Migration { /** * Run the migrations. * * @return void */ public function up ( ) { Schema :: create ( 'authors' , function ( Design $table ) { $tabular array -> increments ( 'id' ) ; $tabular array -> string ( 'name' ) ; $table -> string ( 'email' ) ; $table -> cord ( 'github' ) ; $table -> string ( 'twitter' ) ; $table -> string ( 'location' ) ; $table -> string ( 'latest_article_published' ) ; $table -> timestamps ( ) ; } ) ; } /** * Reverse the migrations. * * @return void */ public role downwardly ( ) { Schema :: dropIfExists ( 'authors' ) ; } } Hither nosotros're simply calculation a few extra columns to the authors tabular array such as social handles, location, and a field for the last_article_published.
At present, go ahead and run the migration like so:
php artisan drift Bank check your database. You should at present accept the authors and migrations tables present.
Permit's create the Writer model. Create an app/Author.php file and add the lawmaking below to it:
app/Author.php
<?php namespace App ; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model ; course Author extends Model { /** * The attributes that are mass assignable. * * @var assortment */ protected $fillable = [ 'proper noun' , 'email' , 'github' , 'twitter' , 'location' , 'latest_article_published' ] ; /** * The attributes excluded from the model's JSON form. * * @var array */ protected $hidden = [ ] ; } In the code above, we made the author attributes mass assignable.
Ready Routes
Routing is fairly straight-forward. Open up routes/web.php and modify it similar so:
<?php /* |-------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Awarding Routes |-------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | Here is where you can register all of the routes for an application. | It is a cakewalk. Simply tell Lumen the URIs it should respond to | and give it the Closure to phone call when that URI is requested. | */ $router -> get ( '/' , function ( ) apply ( $router ) { return $router -> app -> version ( ) ; } ) ; $router -> group ( [ 'prefix' => 'api' ] , function ( ) use ( $router ) { $router -> get ( 'authors' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@showAllAuthors' ] ) ; $router -> go ( 'authors/{id}' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@showOneAuthor' ] ) ; $router -> post ( 'authors' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@create' ] ) ; $router -> delete ( 'authors/{id}' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@delete' ] ) ; $router -> put ( 'authors/{id}' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@update' ] ) ; } ) ; In the code above, we have abstracted the functionality for each route into a controller, AuthorController. Route groups allow you to share route attributes, such as middleware or namespaces, beyond a large number of routes without needing to define those attributes on each road. Therefore, every route will accept a prefix of /api. Next, let's create the Author Controller.
Gear up Author Controller
Create a new file, AuthorController.php in app/Http/Controllers directory and add the post-obit code to information technology like then:
<?php namespace App\Http\Controllers ; use App\Writer ; utilize Illuminate\Http\Request ; class AuthorController extends Controller { public function showAllAuthors ( ) { return response ( ) -> json ( Author :: all ( ) ) ; } public role showOneAuthor ( $id ) { return response ( ) -> json ( Writer :: discover ( $id ) ) ; } public function create ( Asking $request ) { $author = Author :: create ( $asking -> all ( ) ) ; return response ( ) -> json ( $author , 201 ) ; } public function update ( $id , Request $asking ) { $author = Author :: findOrFail ( $id ) ; $author -> update ( $request -> all ( ) ) ; return response ( ) -> json ( $author , 200 ) ; } public function delete ( $id ) { Author :: findOrFail ( $id ) -> delete ( ) ; return response ( 'Deleted Successfully' , 200 ) ; } } Let's clarify the code in a higher place. Starting time, we have use App\Author, which immune u.s.a. to require the Author model that nosotros created before.
Next, nosotros've created the following five methods:
-
showAllAuthors- /GET
-
showOneAuthor- /GET
-
create- /Post
-
update- /PUT
-
delete- /DELETE
These will allow us to use that Author model to interact with author data. For case, if you make a Mail service asking to /api/authors API endpoint, the create function volition exist invoked, and a new entry will be added to the authors table.
Author controller method overview:
-
showAllAuthors- checks for all the author resources
-
create- creates a new author resource
-
showOneAuthor- checks for a single author resource
-
update- checks if an author resources exists and allows the resource to exist updated
-
delete- checks if an author resource exists and deletes it
Controller responses:
-
response ( )- global helper function that obtains an case of the response factory
-
response ( ) - > json ( )- returns the response in JSON format.
-
200- HTTP condition code that indicates the request was successful.
-
201- HTTP status code that indicates a new resources has simply been created.
-
findOrFail- throws a
ModelNotFoundExceptionif no issue is not constitute.
- throws a
Finally, test the API routes with Postman.
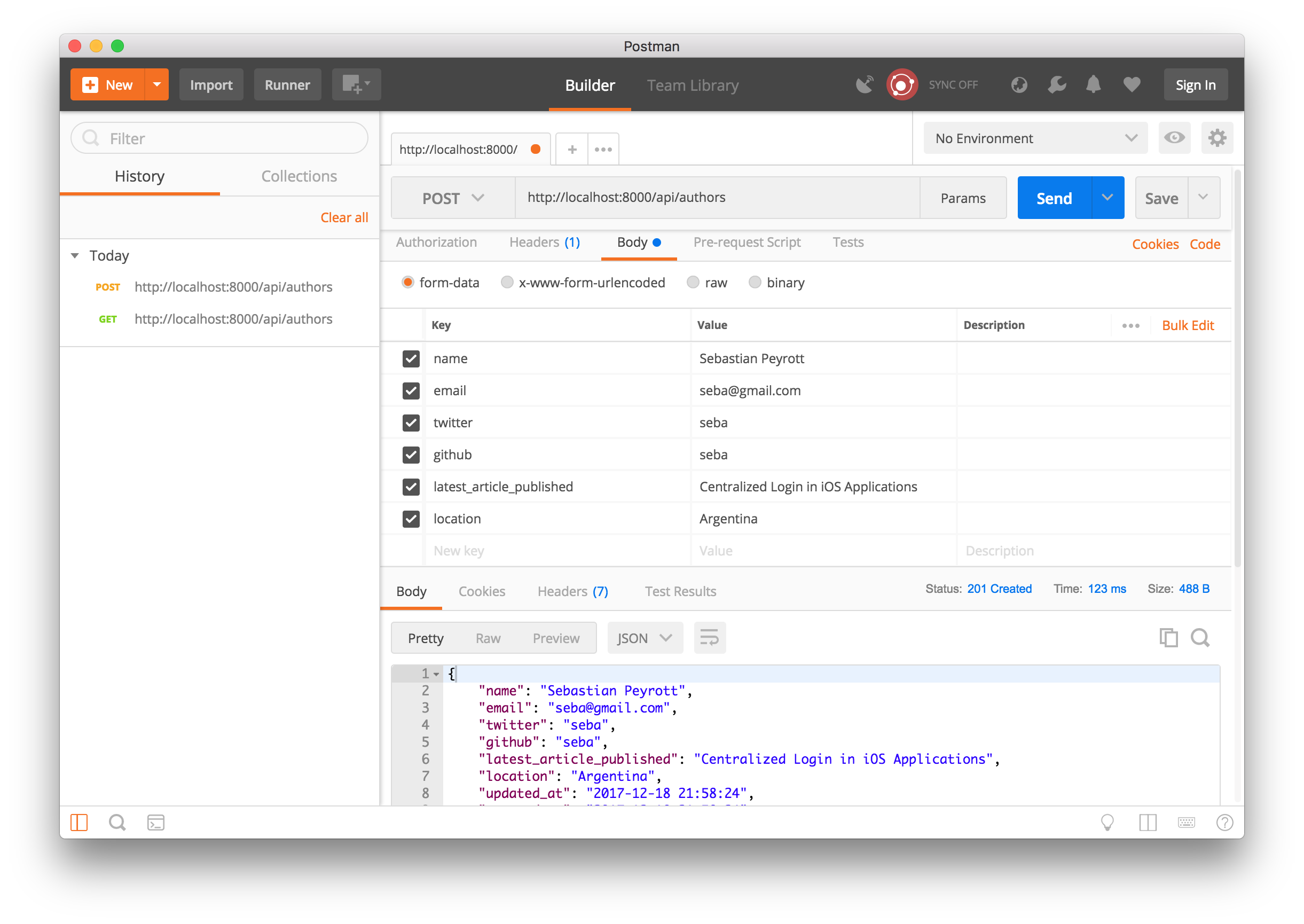
Author Postal service operation - Mail service http: / /localhost: 8000 /api/authors
Make sure you lot take selected POST from the dropdown, and then you can fill the grade data in past clicking on Body then selecting form-information. Fill in a value for name, electronic mail, etc. to create a new writer.
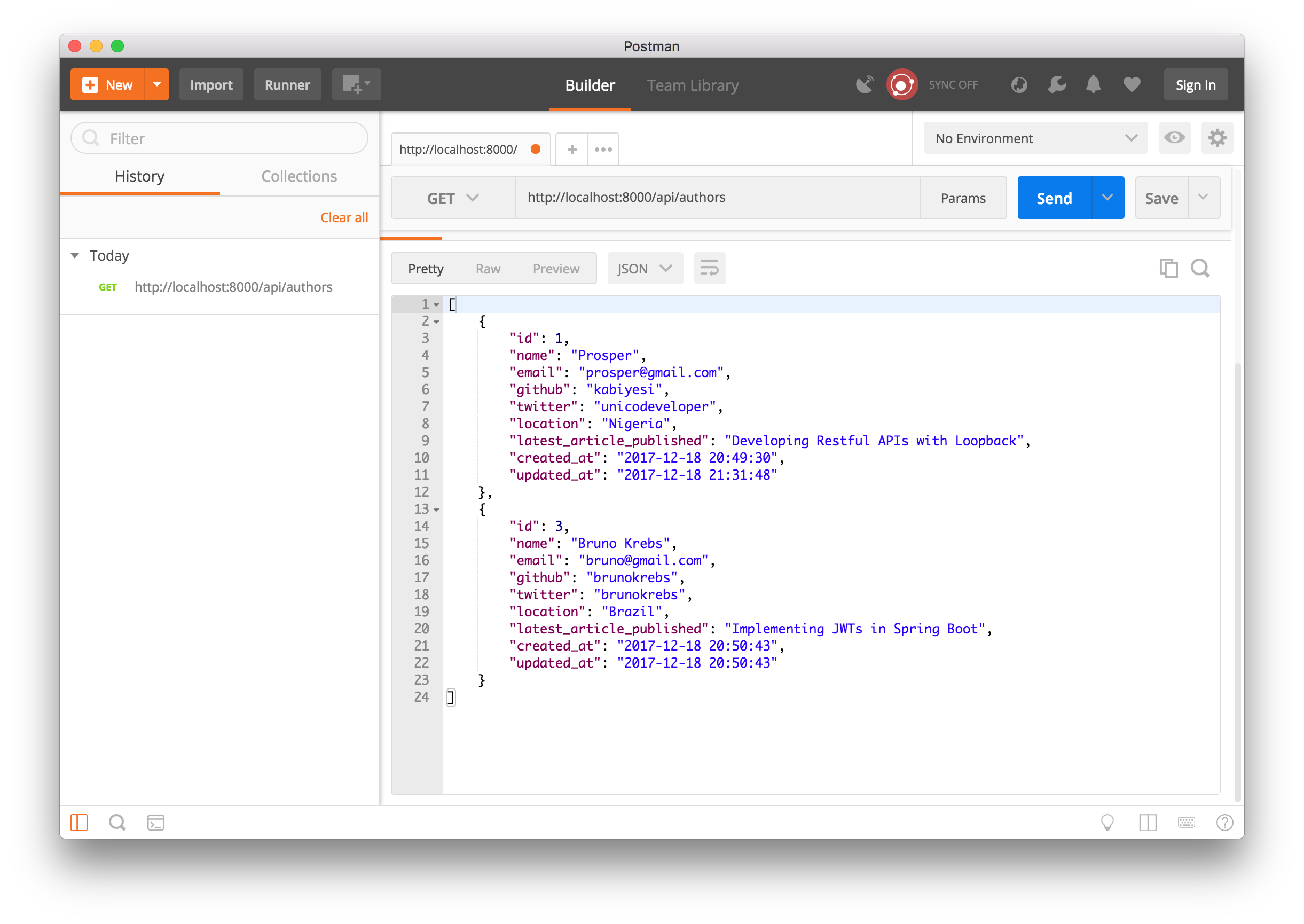
Author Go operation - GET http: / /localhost: 8000 /api/authors
You should now see an array of objects, including the author yous just created plus any others in the database.
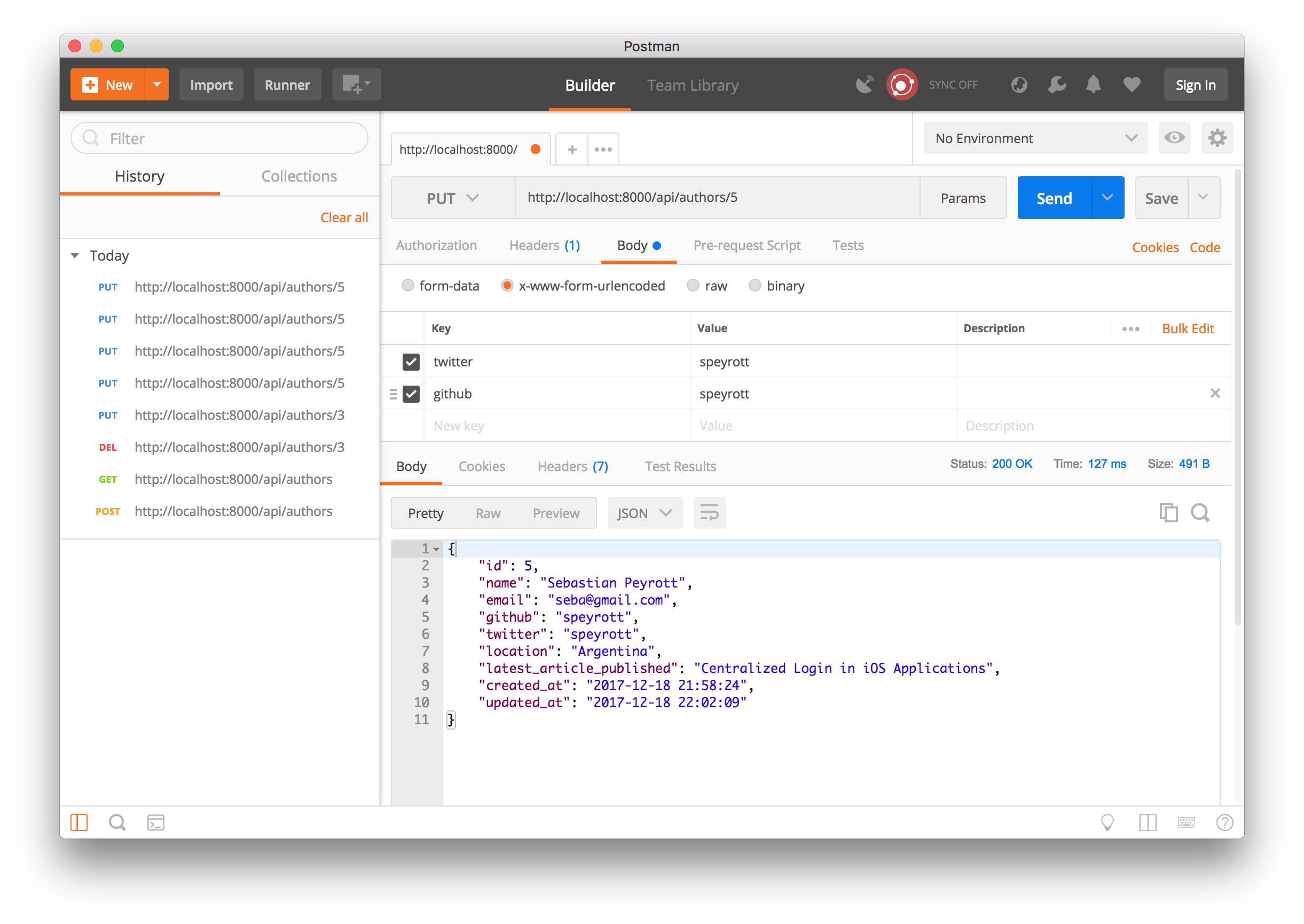
Author PUT operation
The PUT operation allows us to edit an existing author. Find the writer's id in the URL.
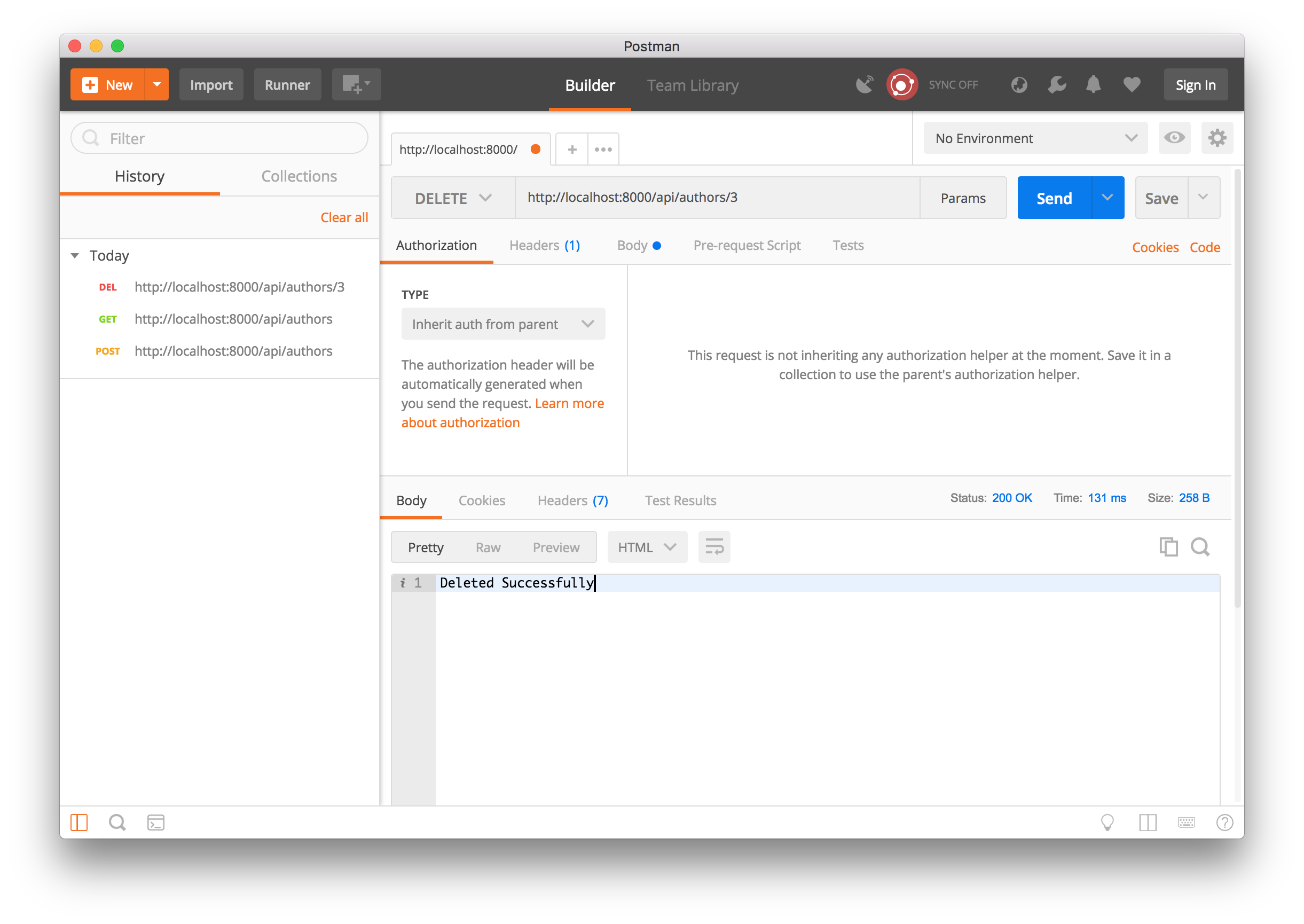
Author DELETE operation
Finally, nosotros can delete a specific author as well.
Now we accept a working API. Awesome!
Lumen API Validation
When developing applications, never trust the user. Ever validate incoming data.
In Lumen, it's very piece of cake to validate your application's incoming information. Lumen provides access to the $this - >validate helper method from within Route closures.
Currently, in our API, nosotros're not checking what people are sending through to our create method. Permit'southward fix that at present.
Open up up the AuthorController file and modify the create method like this:
// ... public part create ( Request $request ) { $this -> validate ( $request , [ 'proper noun' => 'required' , 'email' => 'required|electronic mail|unique:authors' , 'location' => 'required|alpha' ] ) ; $author = Author :: create ( $request -> all ( ) ) ; render response ( ) -> json ( $writer , 201 ) ; } // ... Now exam the API Mail route with Postman.
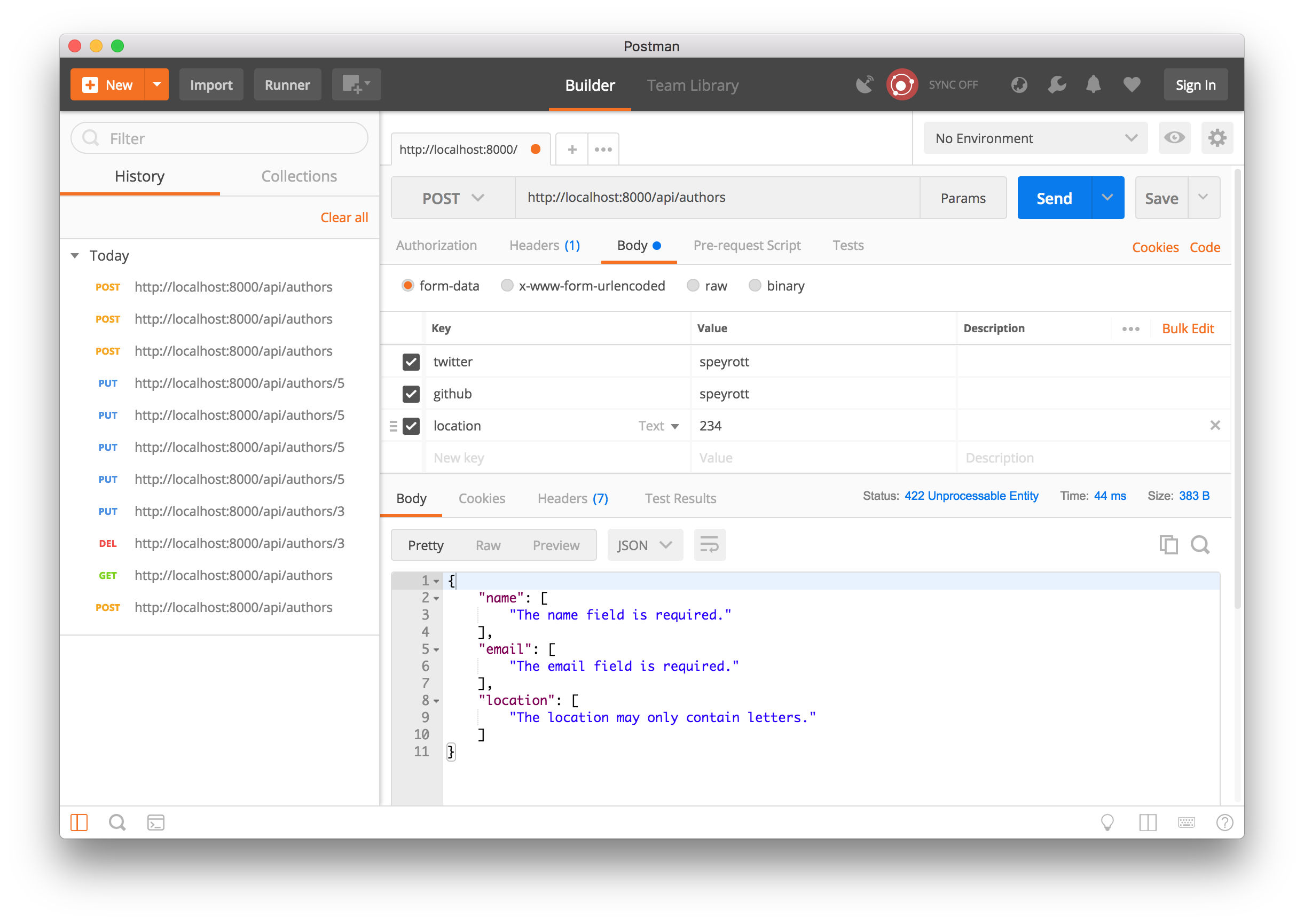
It validated the incoming requests and returned the appropriate error bulletin.
- proper name, e-mail, and location were required. In testing the API, name and email were non provided.
- email was required to be in email format.
- location was required to be entirely alphabetic characters,
alpha. Naught more than. Numbers were provided as the value for location.
Notation: Always validate incoming data. Never trust your users!
Check out a plethora of validation rules that you lot can use with Lumen.
Securing the Authors API with Auth0
Correct at present, an application tin can make requests to any of the endpoints nowadays in our API. In a real-earth scenario, nosotros would want to restrict our API then that but certain authorized users have the power to practise this. A few things need to happen here.
- A user signs in with their credentials (to prove who they are, i.e., authenticate)
- If the user is authorized to apply the API, the application is issued an API admission token
- Whenever an API request is made, the awarding volition send that API access token along with the request
- If the access token is valid, the API will reply with the requested data
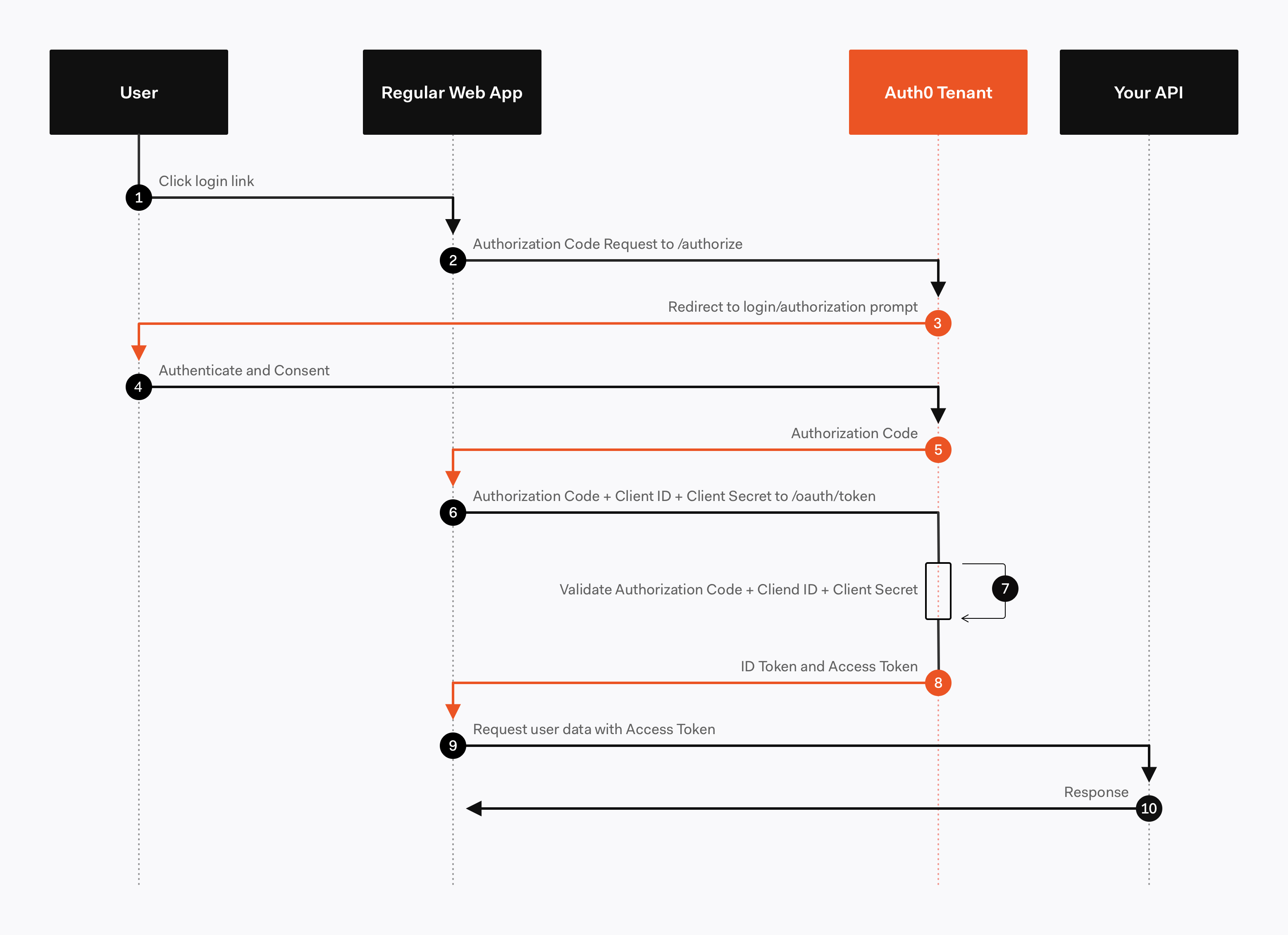
In this tutorial, nosotros're going to focus on what happens in step 4 of that list (step nine-10 in the diagram). Since nosotros're merely edifice the backend API here, y'all'll need to create a separate forepart-end to attain the first two steps. Here is an awesome instance of how y'all can do that using Auth0 with React.
For now, allow's focus on generating access tokens using JSON Web Tokens.
JSON Spider web Token, commonly known as JWT, is an open standard for creating JSON-based admission tokens that make some claim, commonly authorizing a user or exchanging information. This technology has gained popularity over the past few years because it enables backends to accept requests simply by validating the contents of these JWTs.
JWTs can be used for authority or information exchange. In this tutorial, we'll be using JWTs to grant authorization to applications (users) using our API.
Whenever the user wants to access a protected route or resources (an endpoint), the user agent must send the JWT, usually in the Authorization header using the Bearer schema, along with the asking.
When the API receives a request with an access token, the first thing information technology needs to practice is validate the token. If the validation fails, then the asking must be rejected.
For more information about JSON Spider web Tokens, cheque out our free ebook below.

We volition brand use of Auth0 to effect our access tokens. With Auth0, nosotros only have to write a few lines of lawmaking to get an in-depth identity direction solution which includes:
- Unmarried sign-on
- User management
- Back up for social identity providers (similar Facebook, GitHub, Twitter, etc.)
- Enterprise (Active Directory, LDAP, SAML, etc.)
- Your ain database of users
If you haven't washed then yet, this is a skilful fourth dimension to sign upward for a free Auth0 account.
Try out the most powerful authentication platform for free.Get started →
Once you have your Auth0 account, go ahead and create a new API in the dashboard. An API is an entity that represents an external resources, capable of accepting and responding to requests made by clients, such every bit the authors API nosotros but made.
Auth0 offers a generous free tier to go started with modern authentication.
Login to your Auth0 management dashboard and create a new API customer.
Click on the APIs carte du jour item and then the Create API push button.
Create a New API 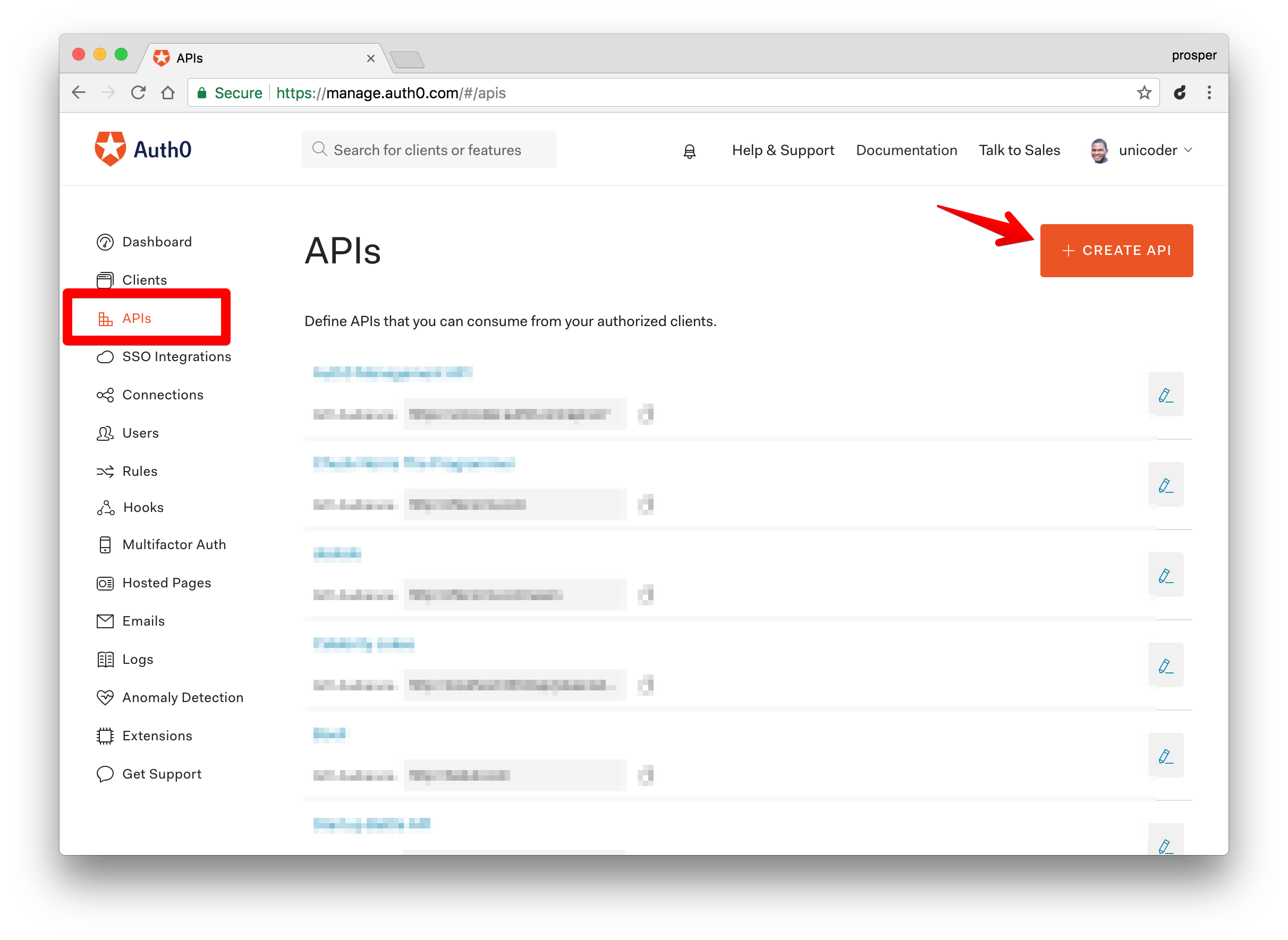
Adjacent, you lot will need to requite your API a Name and an Identifier. The Name can be anything you cull, so brand it as descriptive every bit yous want. The Identifier will be used to specify your API and cannot be changed once set. We'll be using information technology as an audience later on when configuring the access token verification.
Hither'due south my setup for the author's API:
- Proper name: Authors API
- Identifier: https://authorsapi.com.
- Signing algorithm: RS256
Once yous have yours filled out, click on the Create API button.
Creating the Authors API 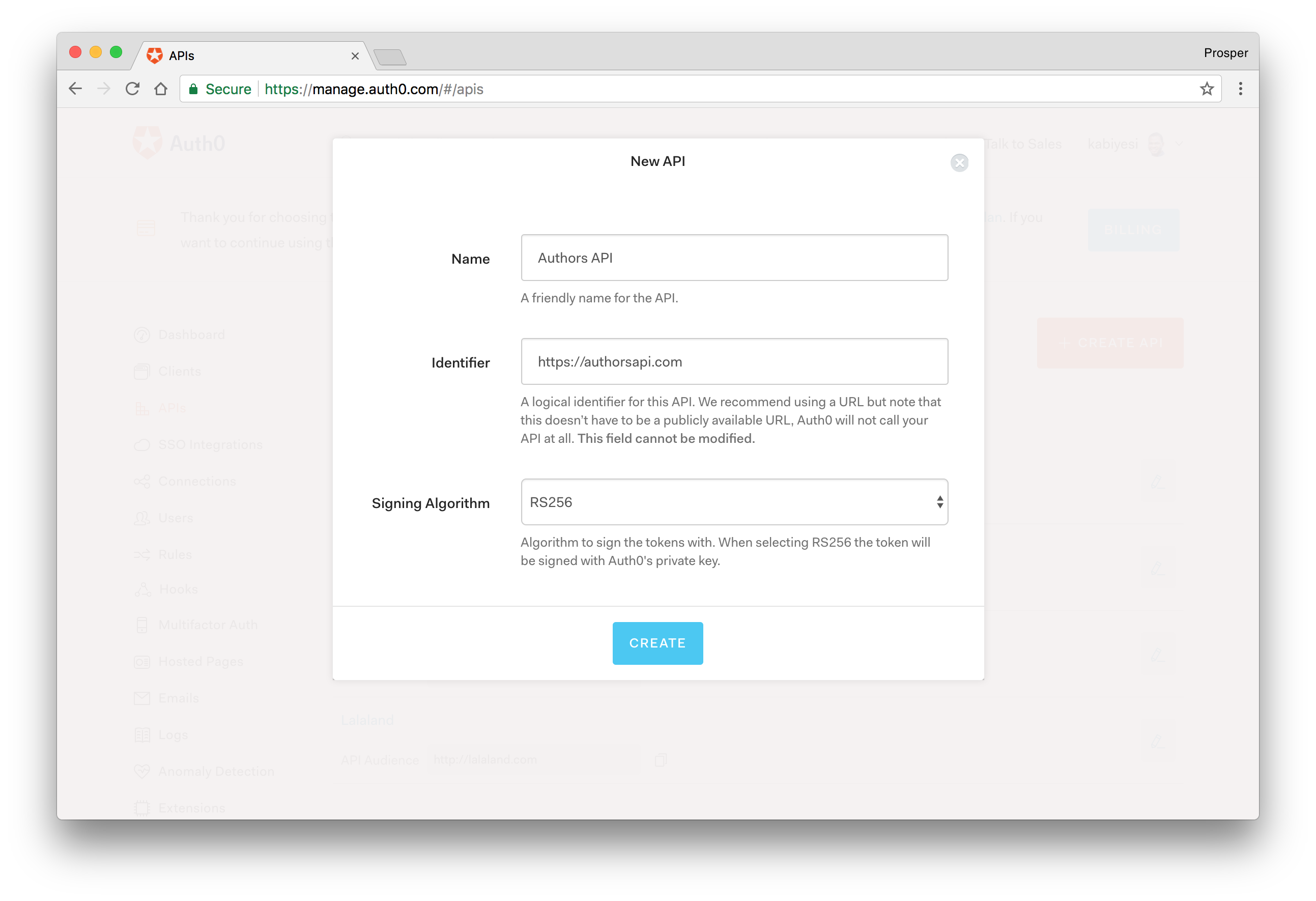
Side by side head over to your terminal and install the Auth0 PHP SDK in your project's root directory:
composer require auth0/auth0-php Setting up environs variables
In this section, we're going to create the middleware to validate access tokens. The middleware volition use some environment variables, so let's set those upward first.
Open up .env and add the following:
AUTH0_DOMAIN =https: / / your-domain.auth0.com / AUTH0_AUD =https: / /authorsapi.com Replace these values with your own from the Auth0 dashboard.
AUTH0_DOMAIN
To find your domain, click on APIs > Authors API > Quick Showtime > PHP in the dashboard. Copy the value listed for authorized_iss and paste it into .env as AUTH0_DOMAIN .
When filling in the
AUTH0_DOMAINvalue, make certain you add the trailing slash:https: / / xyz.auth0.com /.
AUTH0_AUD
Y'all can find this value in the Auth0 dashboard in the same place as the domain:
APIs > Quick Start > PHP .
Copy the value listed for valid_audiences and paste information technology in for AUTH0_AUD . If you followed the naming conventions of this tutorial, it would be https: / /authorsapi.com.
Create the Auth0 Middleware
Create a new middleware file, Auth0Middleware.php, in the app/Http/Middleware directory. Add the following code to it:
<?php namespace App\Http\Middleware ; use Closure ; utilise Auth0\SDK\Exception\InvalidTokenException ; use Auth0\SDK\Helpers\JWKFetcher ; apply Auth0\SDK\Helpers\Tokens\AsymmetricVerifier ; apply Auth0\SDK\Helpers\Tokens\TokenVerifier ; class Auth0Middleware { /** * Run the request filter. * * @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request * @param \Closure $next * @return mixed */ public function handle ( $request , Closure $next ) { $token = $asking -> bearerToken ( ) ; if ( ! $token ) { return response ( ) -> json ( 'No token provided' , 401 ) ; } $this -> validateToken ( $token ) ; return $next ( $request ) ; } public part validateToken ( $token ) { try { $jwksUri = env ( 'AUTH0_DOMAIN' ) . '.well-known/jwks.json' ; $jwksFetcher = new JWKFetcher ( null , [ 'base_uri' => $jwksUri ] ) ; $signatureVerifier = new AsymmetricVerifier ( $jwksFetcher ) ; $tokenVerifier = new TokenVerifier ( env ( 'AUTH0_DOMAIN' ) , env ( 'AUTH0_AUD' ) , $signatureVerifier ) ; $decoded = $tokenVerifier -> verify ( $token ) ; } catch ( InvalidTokenException $e ) { throw $e ; } ; } } This middleware checks if a request is made with a valid access token. In the adjacent step, we'll utilise this middleware to all of our routes that we want to protect. That style, before the request is executed, the middleware will run and cheque for the valid access token.
Let's look at how we validate the access token.
The handle ( ) method showtime takes the asking and grabs the access token. If it doesn't exist, an error is returned, and the request fails.
If the token does be, we need to check that it's valid, which is done in validateToken ( ) .
First, we grab the JSON Web Primal Set URI.
$jwksUri = env ( 'AUTH0_DOMAIN' ) . '.well-known/jwks.json' ; The JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) is a set of keys that contains the public keys used to verify any JSON Web Token (our admission token) issued by the authorization server and signed using the RS256 signing algorithm.
If you're curious, yous can find your public JWKS at the url: your Auth0 domain + '.well-known/jwks.json'. Employ the domain you lot used in your .env file. Here's mine: https://demo-apps.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json.
Next, we're using JWKFetcher ( ) to pull the keys from that URI. The start parameter accepts a cache handler to salvage the keys to the cache. We haven't set one up, so just leave it zippo .
$jwksFetcher = new JWKFetcher ( null , [ 'base_uri' => $jwksUri ] ) ; Next up is the $signatureVerifier:
$signatureVerifier = new AsymmetricVerifier ( $jwksFetcher ) ; This is how our application will verify the signature of the JWT. Auth0 has a private key that generated the signature, then we have to use the public key to validate that the sender of the JWT is who they say they are.
Note: The
AsymmetricVerifier ( )is used for the RS256 signing algorithm. If you're using HS256, then useSymmetricVerifier ( )and laissez passer it the Auth0 customer surreptitious instead. You can detect the client undercover in your Auth0 dashboard.E.m.
$signature_verifier = new SymmetricVerifier ( env ( 'AUTH0_CLIENT_SECRET' ) ) ;
Subsequently setting up the signature verification, we must now validate the residue of the token.
$tokenVerifier = new TokenVerifier ( env ( 'AUTH0_DOMAIN' ) , env ( 'AUTH0_AUD' ) , $signatureVerifier ) ; This takes iii parameters:
- Auth0 domain — the token issuer
- Auth0 audience — the API identifier
- Signature verifier — the token signature verifier gear up upwards previously
It will verify that the token exists, the signature is verified, the token algorithm is supported, and all JWT claims are valid.
If all of this passes, the token is decoded and the middleware allows the HTTP request to execute.
Assign middleware to routes
Now that the middleware is set up, we need to add information technology to our routes. The showtime step is to assign the middleware a short-hand key in bootstrap/app.php file'due south call to the $app- > routeMiddleware ( ) method.
Go alee and open up bootstrap/app.php and uncomment this line of code:
... // $app->routeMiddleware([ // 'auth' => App\Http\Middleware\Authenticate::class, // ]); ... Once uncommented, replace the Authenticate: : form with Auth0Middleware: : class like so:
$app -> routeMiddleware ( [ 'auth' => App\Http\Middleware\Auth0Middleware :: class , ] ) ; This will let us to apply the Auth0Midddleware that we just created. And now we can use the middleware key in the road options array in the routes/web.php file like so:
... $router -> group ( [ 'prefix' => 'api' , 'middleware' => 'auth' ] , part ( ) use ( $router ) { $router -> get ( 'authors' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@showAllAuthors' ] ) ; $router -> go ( 'authors/{id}' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@showOneAuthor' ] ) ; $router -> post ( 'authors' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@create' ] ) ; $router -> delete ( 'authors/{id}' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@delete' ] ) ; $router -> put ( 'authors/{id}' , [ 'uses' => 'AuthorController@update' ] ) ; } ) ; Now, if a request is made to any endpoint, it first runs the Auth0Middleware. If the request doesn't have a valid access token or no token at all, it returns an error. Permit's endeavor all of this out.
Accessing any endpoint without an authorization header
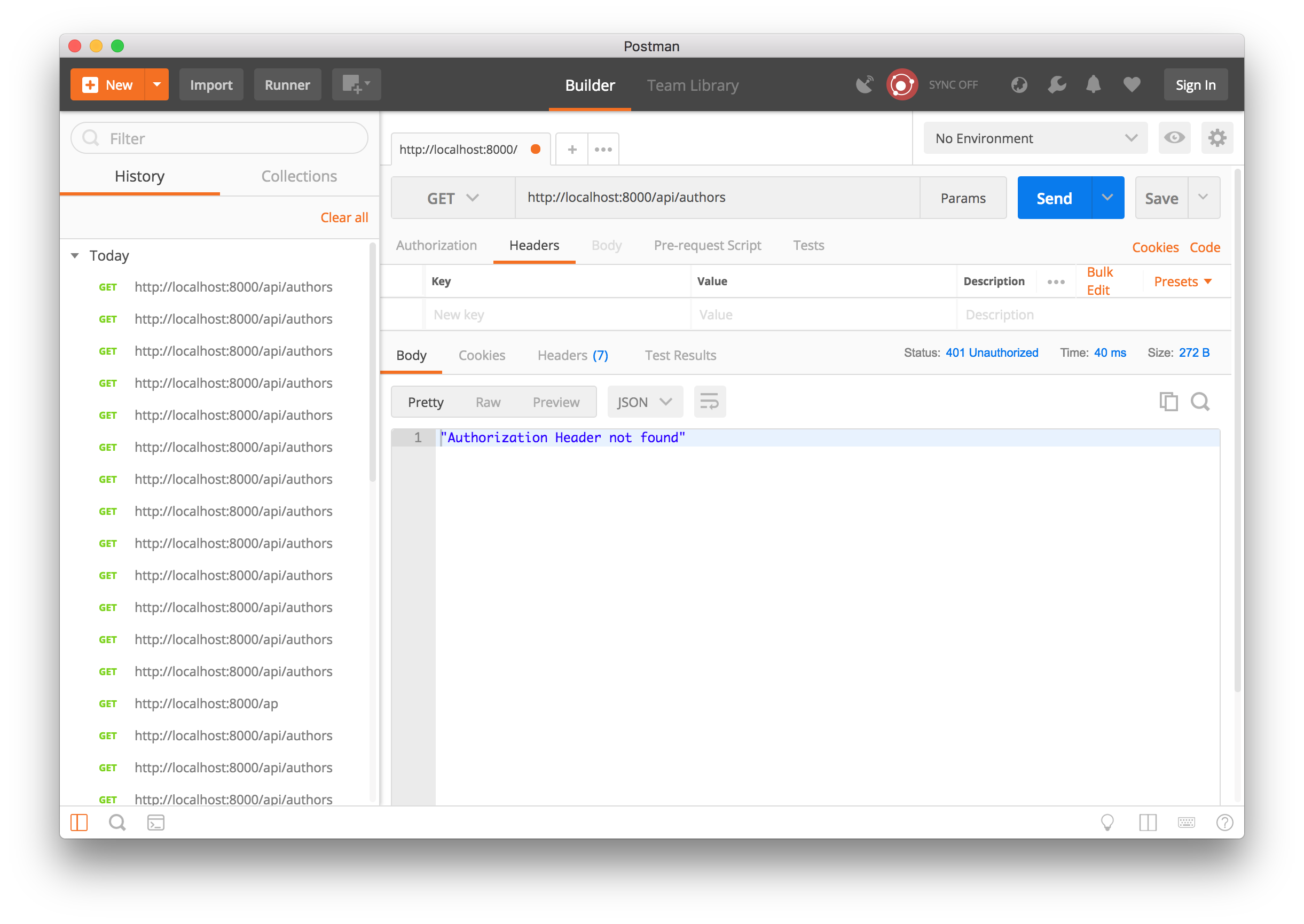
Accessing any endpoint without whatever token provided
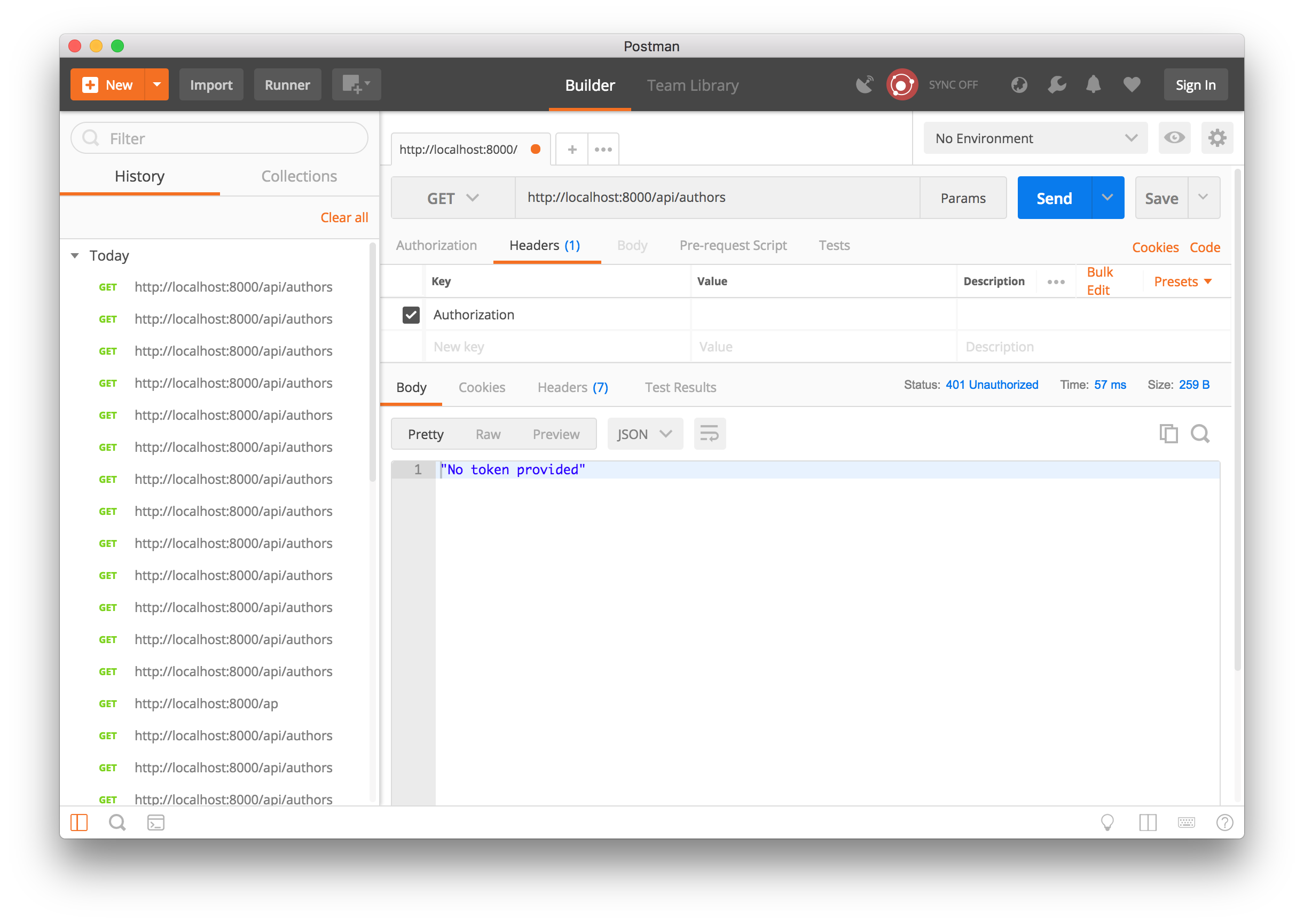
Accessing any endpoint without a valid access token
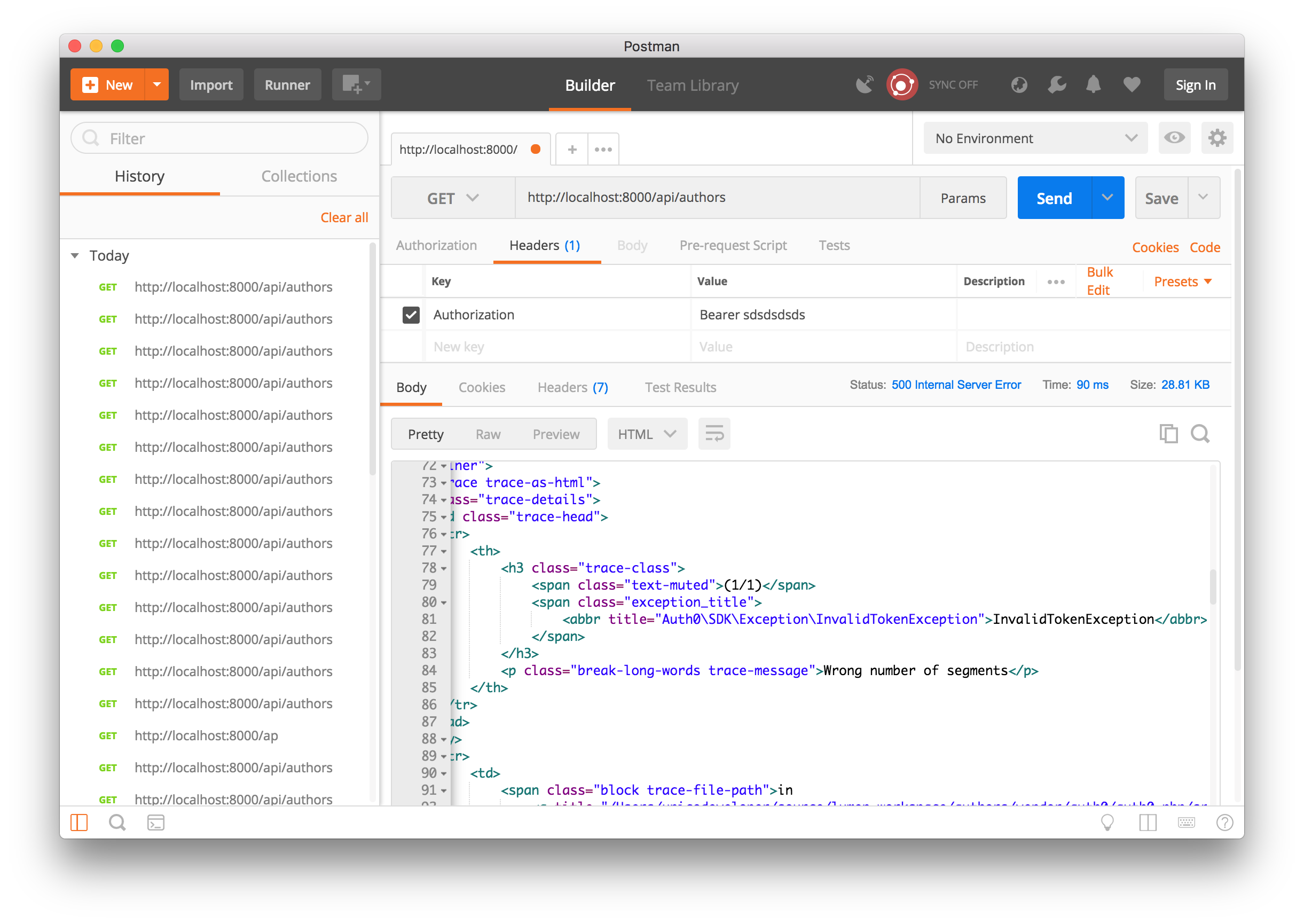
Now, let'southward test it with a valid access token. Head over to the test tab of your newly created API on your Auth0 dashboard.
Grab the Access token from the Test tab
Grab the Access Token
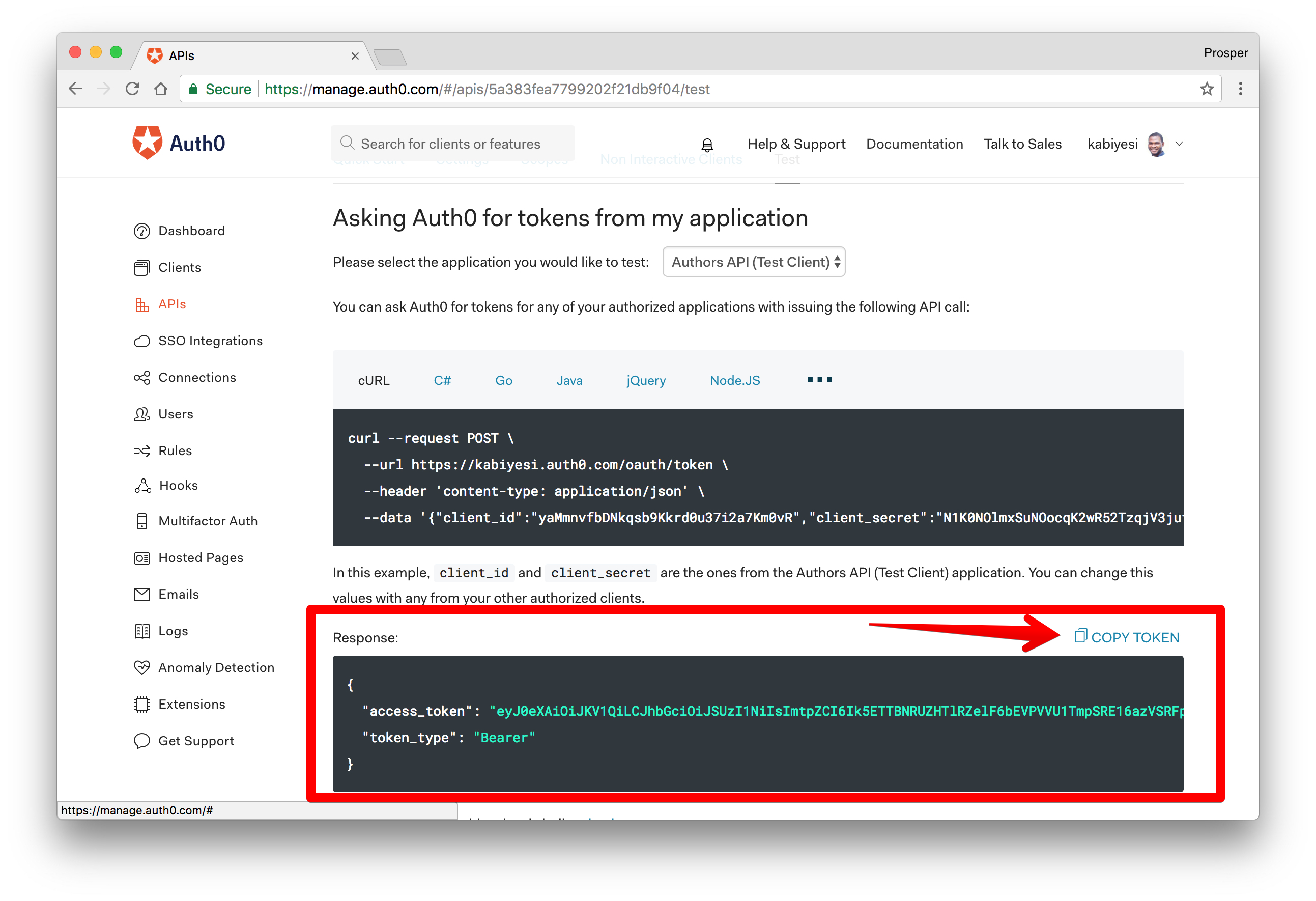
Now use this access token in Postman past sending it as an Authorization header to make a Postal service request to api/authors endpoint.
Accessing the endpoint deeply
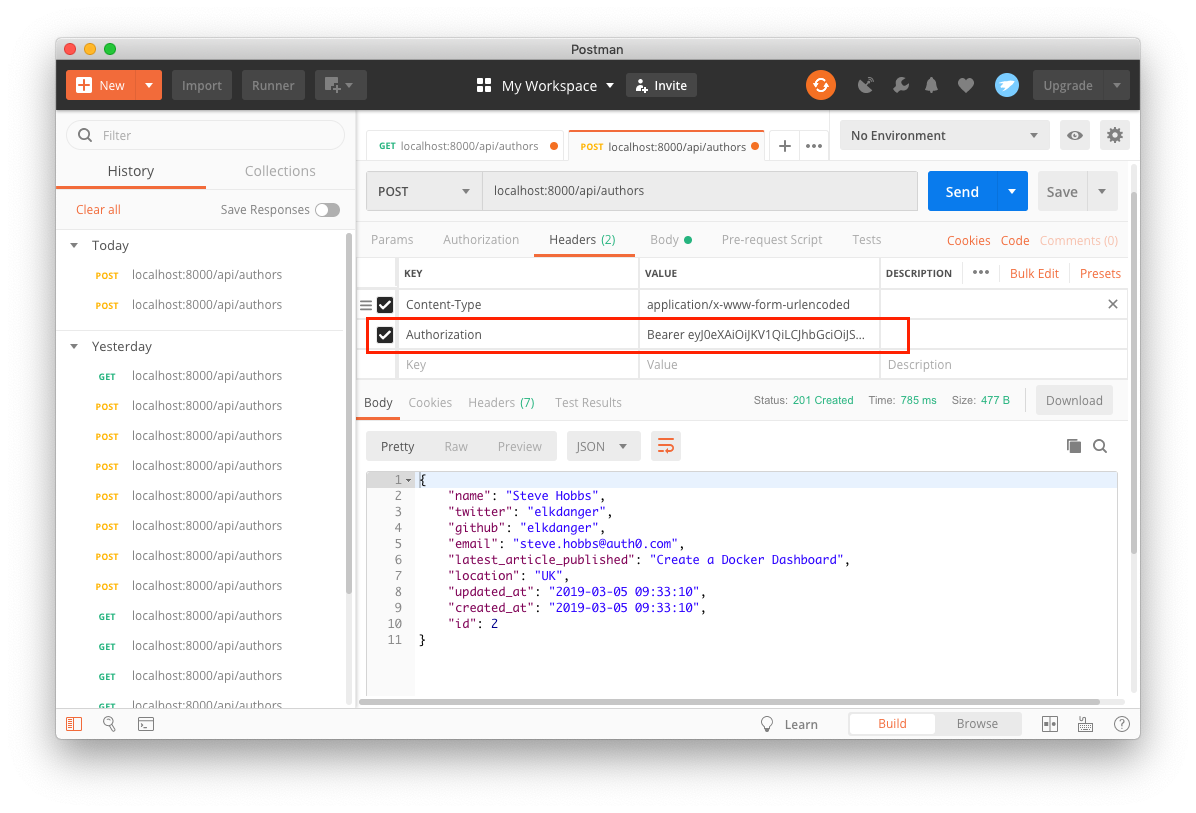
Information technology validates the access token and successfully makes the Post request.
Notation: If you're getting a bulletin that the token cannot be trusted, try calculation a abaft slash to
AUTH0_DOMAINin.env, e.g.,https: / / xyz.auth0.com /
Calculation permissions
Currently, this single access token volition allow an application to run any requests, equally long as information technology has a valid token. You may desire to eventually issue sure permissions with the access token. Let's attempt it out.
In the Auth0 dashboard, find the API nosotros've been using and and so click on Permissions. Create a new scope that volition grant permission to create a new writer (east.g., create:authors). Then add a brusque description of what that scope does and click "Add".
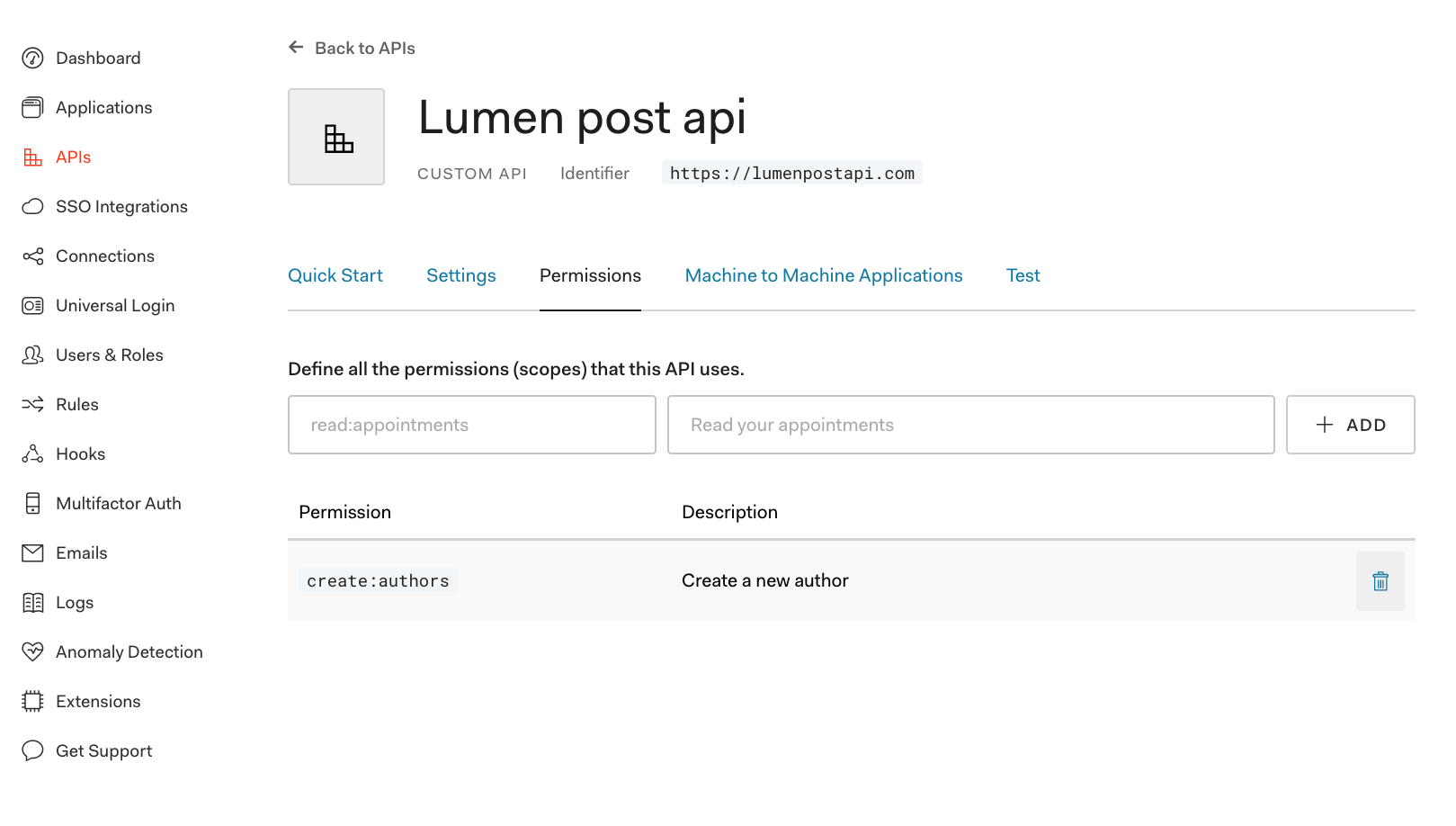
Now our API expects that when an application makes a request to create a new author, it must as well ship an access token that includes the create:authors scope. To check for this, we need to add together middleware that checks the scope in the access token. Open up Auth0Middleware.php and supersede information technology with:
// app/Http/Middleware/Auth0Middleware.php <?php namespace App\Http\Middleware ; use Closure ; use Auth0\SDK\Exception\InvalidTokenException ; use Auth0\SDK\Helpers\JWKFetcher ; use Auth0\SDK\Helpers\Tokens\AsymmetricVerifier ; apply Auth0\SDK\Helpers\Tokens\TokenVerifier ; course Auth0Middleware { /** * Run the asking filter. * * @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request * @param \Closure $next * @return mixed */ public part handle ( $request , Closure $next , $scopeRequired = nix ) { $token = $asking -> bearerToken ( ) ; if ( ! $token ) { render response ( ) -> json ( 'No token provided' , 401 ) ; } $decodedToken = $this -> validateAndDecode ( $token ) ; if ( $scopeRequired && ! $this -> tokenHasScope ( $decodedToken , $scopeRequired ) ) { return response ( ) -> json ( [ 'bulletin' => 'Bereft scope' ] , 403 ) ; } render $adjacent ( $request ) ; } public function validateAndDecode ( $token ) { try { $jwksUri = env ( 'AUTH0_DOMAIN' ) . '.well-known/jwks.json' ; $jwksFetcher = new JWKFetcher ( naught , [ 'base_uri' => $jwksUri ] ) ; $signatureVerifier = new AsymmetricVerifier ( $jwksFetcher ) ; $tokenVerifier = new TokenVerifier ( env ( 'AUTH0_DOMAIN' ) , env ( 'AUTH0_AUD' ) , $signatureVerifier ) ; return $tokenVerifier -> verify ( $token ) ; } grab ( InvalidTokenException $due east ) { throw $e ; } ; } /** * Check if a token has a specific telescopic. * * @param \stdClass $token - JWT access token to cheque. * @param string $scopeRequired - Telescopic to check for. * * @return bool */ protected function tokenHasScope ( $token , $scopeRequired ) { if ( empty ( $token [ 'scope' ] ) ) { return false ; } $tokenScopes = explode ( ' ' , $token [ 'telescopic' ] ) ; render in_array ( $scopeRequired , $tokenScopes ) ; } } A few changes were made hither.
The first thing to note is we added another parameter, scopeRequired, to the handle ( ) method. This is ready to null by default, since most of our routes won't require the create:author permission. Later in our routes, nosotros'll specify when information technology is required.
// ... public role handle ( $request , Closure $side by side , $scopeRequired = null ) { // ... } // ... Next, nosotros get the token that was validated and decoded in validateAndDecode ( ) :
// ... $decodedToken = $this -> validateAndDecode ( $token ) ; // ... Next, nosotros bank check if the scope is required for this request. If it is, we use that decoded token to check if the telescopic exists. If so, the request continues, only if non, nosotros send an Insufficient telescopic message instead.
if ( $scopeRequired && ! $this -> tokenHasScope ( $decodedToken , $scopeRequired ) ) { return response ( ) -> json ( [ 'message' => 'Bereft telescopic' ] , 403 ) ; } We likewise added the method tokenHasScope ( ) , which is what'southward doing the check for that specific scope in the previous if statement.
protected function tokenHasScope ( $token , $scopeRequired ) { if ( empty ( $token [ 'scope' ] ) ) { return false ; } $tokenScopes = explode ( ' ' , $token [ 'scope' ] ) ; return in_array ( $scopeRequired , $tokenScopes ) ; } It grabs all of the scopes in the token, splits each scope as an assortment particular, and searches the array for the required telescopic.
Finally, nosotros need to add together this scope check middleware to our road for creating a new writer. Open up up routes/spider web.php and modify the post route every bit follows:
// routes/web.php // ... $router -> group ( [ 'prefix' => 'api' , 'middleware' => 'auth' ] , function ( ) apply ( $router ) { // ... $router -> post ( 'authors' , [ 'middleware' => 'auth:create:authors' , 'uses' => 'AuthorController@create' ] ) ; // ... } ) ; Now, if you attempt to create a new writer in Postman using that same token as before, you'll receive the "Bereft scope" message.
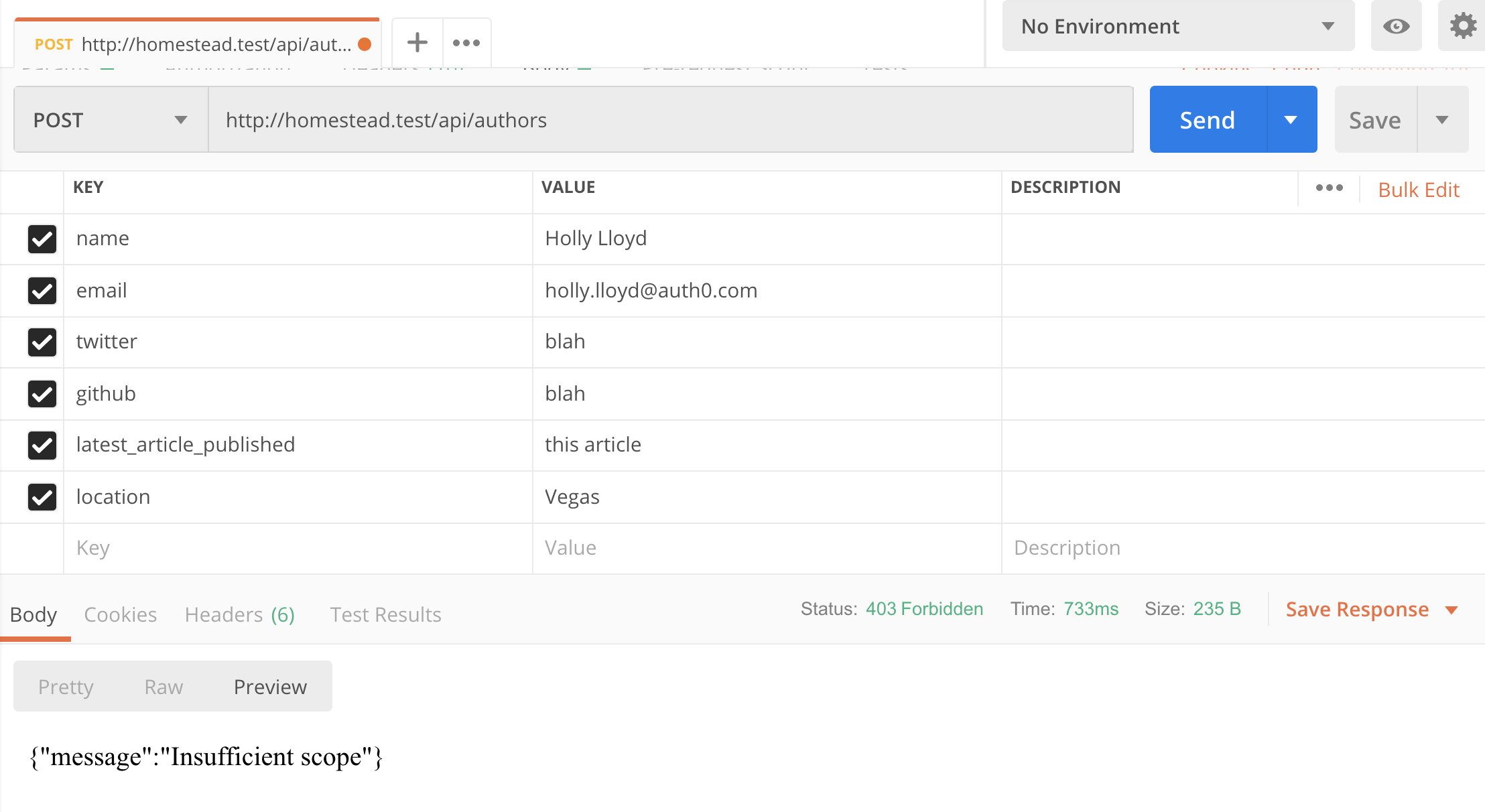
To exam that information technology works, make sure you lot're on the page with your API in the Auth0 dashboard and so get to the Permissions tab. Click on Car to Machine Applications and find the API Application y'all've been using. Make sure the Authorized toggle is on and then click on the arrow. At present select the create:authors scope and printing "Update".
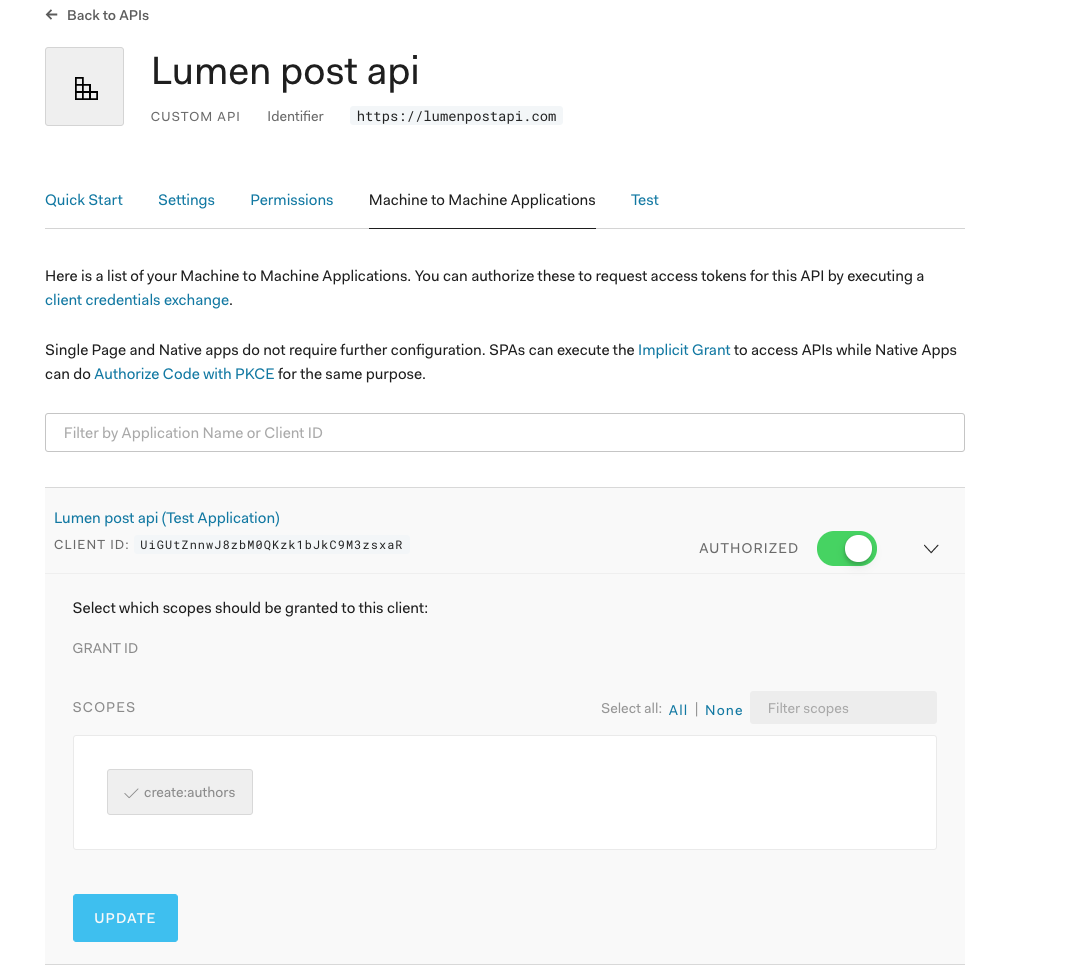
Now the permission for create:authors has been added to our test token. Head dorsum over to the "Exam" tab and press "Copy token" to get the updated one.
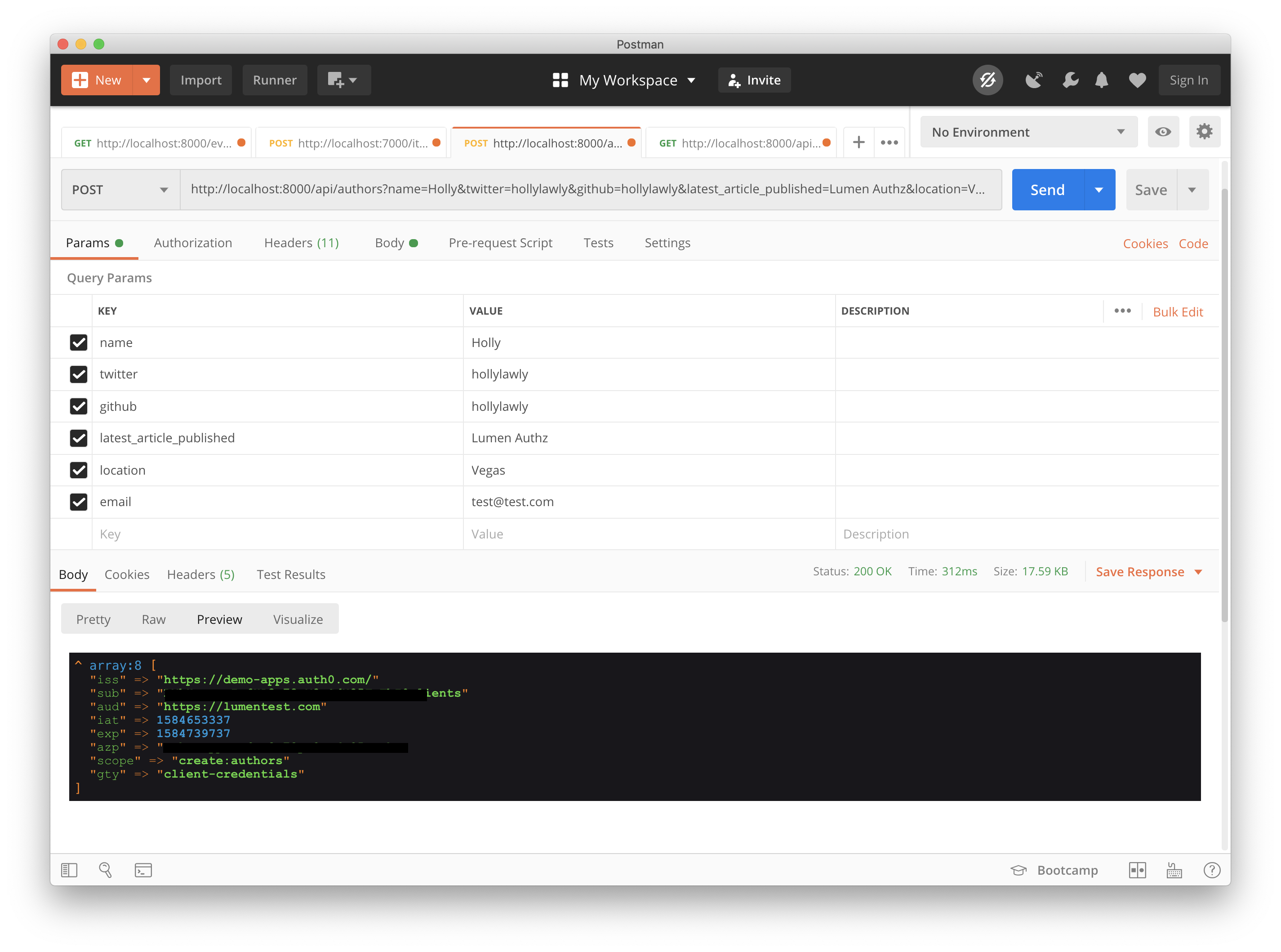
Paste that token into the Authorization header every bit you did before (make sure you have Bearer earlier it), try the POST request once more, and now it should have worked!
If yous'd like to see what the decoded admission token looks like, simply add dd ($decodedToken) ; inside the handle ( ) method in app/Http/Middleware/Auth0Middleware.php correct after the $decodedToken variable is alleged. So just run that POST request one more than time in Postman, and you'll encounter the contents of the token, including the scope. Pretty cool! Just brand certain yous delete that exam line in a real application.
Calculation a front end-stop
This is just an instance of how to create the API admission tokens. In one case y'all're ready to really consequence and use them, y'all need to create a front-cease. Here are some astonishing React and Vue.js authentication tutorials that cover how you tin accomplish that.
Conclusion
Well done! You have learned how to build a residual API with the powerful PHP micro-framework Lumen and secure it using JWTs. Demand to use PHP to build your API or micro-service? I'd bet on Lumen every bit the tool of choice for speed and ease of use.
As you lot've seen, Auth0 can assistance secure your API with ease. Auth0 provides more than but username-password authentication. It provides features similar multifactor auth, breached password detection, anomaly detection, enterprise federation, single sign-on (SSO), and more than.
Sign upward
today so you can take the stress out of authentication and instead focus on building unique features for your app.
Please, let me know if you have any questions in the comment section. 😊
Source: https://auth0.com/blog/developing-restful-apis-with-lumen/
0 Response to "Lumen Connection Fail. Please Try Again."
Post a Comment